The Spectator Issue 414, Wednesday, June 25, 1712
By
Joseph Addison
--------------—Alterius sic
Altera poscit opem res et conjurat amicè.AviaAvia"Each demands the help of another." From the Roman poet Horace, Ars Poetica.
Wednesday June 25. 1712.
If we consider the Works of Nature and Art, as they are qualified to entertain the Imagination, we shall find the last very defective, in Comparison of the former; for though they may sometimes appear as Beautiful or Strange, they can have nothing in them of that Vastness and Immensity, which afford so great an Entertainment to the Mind of the Beholder. The one may be as Polite and Delicate as the other, but can never shew her self so August and Magnificent in the Design. There is something more bold and masterly in the rough careless Strokes of Nature, than in the nice Touches and Embellishments of Art. The Beauties of the most stately Garden or Palace lie in a narrow Compass, the Imagination immediately runs them over, and requires something else to gratifie her; but, in the wide Fields of Nature, the Sight wanders up and down without Confinement, and is fed with an infinite variety of Images, without any certain Stint or Number. For this Reason we always find the Poet in Love with a Country-Life, where Nature appears in the greatest Perfection, and furnishes out all those Scenes that are most apt to delight the Imagination.
Scriptorum chorus omnis amat nemus & fugit Urbes. Hor.HorHor"Every chorus of writers loves the grove and flees the cities." from one of the Epistles by the Latin poet Horace. Hic Secura quies, & nescia fallere vita, Dives opum variarum; hic latis otia fundis, Speluncæ, vivique lacus, hic frigida Tempe, Mugitusque boum, mollesque sub arbore somni. Virg.VirgVirg"The peace of broad domains, caverns, and natural lakes, and cool vales--all are theirs." from book II of the Georgics by the Roman poet Virgil. Loeb Classical Library translation.But tho' there are several of these wild Scenes, that are more delightful than any artificial Shows; yet we find the Works of Nature still more pleasant, the more they resemble those of Art: For in this case our Pleasure rises from a double Principle; from the Agreeableness of the Objects to the Eye, and from their Similitude to other Objects: We are pleased as well with comparing their Beauties, as with surveying them, and can represent them to our Minds, either as Copies or Originals. Hence it is that we take Delight in a Prospect which is well laid out, and diversified with Fields and Meadows, Woods and Rivers; in those accidental LandskipsLandskipsLandskipsLandscapes of Trees, Clouds and Cities, that are sometimes found in the Veins of Marble; in the curious Fret-work of Rocks and Grottos; and, in a Word, in any thing that hath such a Variety or Regularity as may seem the Effect of Design, in what we call the Works of Chance.
If the Products of Nature rise in Value, according as they more or less resemble those of Art, we may be sure that artificial Works receive a greater Advantage from their Resemblance of such as are natural; because here the Similitude is not only pleasant, but the Pattern more perfect. The prettiest Landskip I ever saw, was one drawn on the Walls of a dark Room, which stood opposite on one side to a navigable River, and on the other to a Park. The Experiment is very common in Opticks.cameracameraLandscape. Addison is describing a camera obscura, a dark room or a box with a pinhole on one side through which light is let in; on the opposite side or wall, an image of what is outside the room or box appears, upside -down, as in this image. 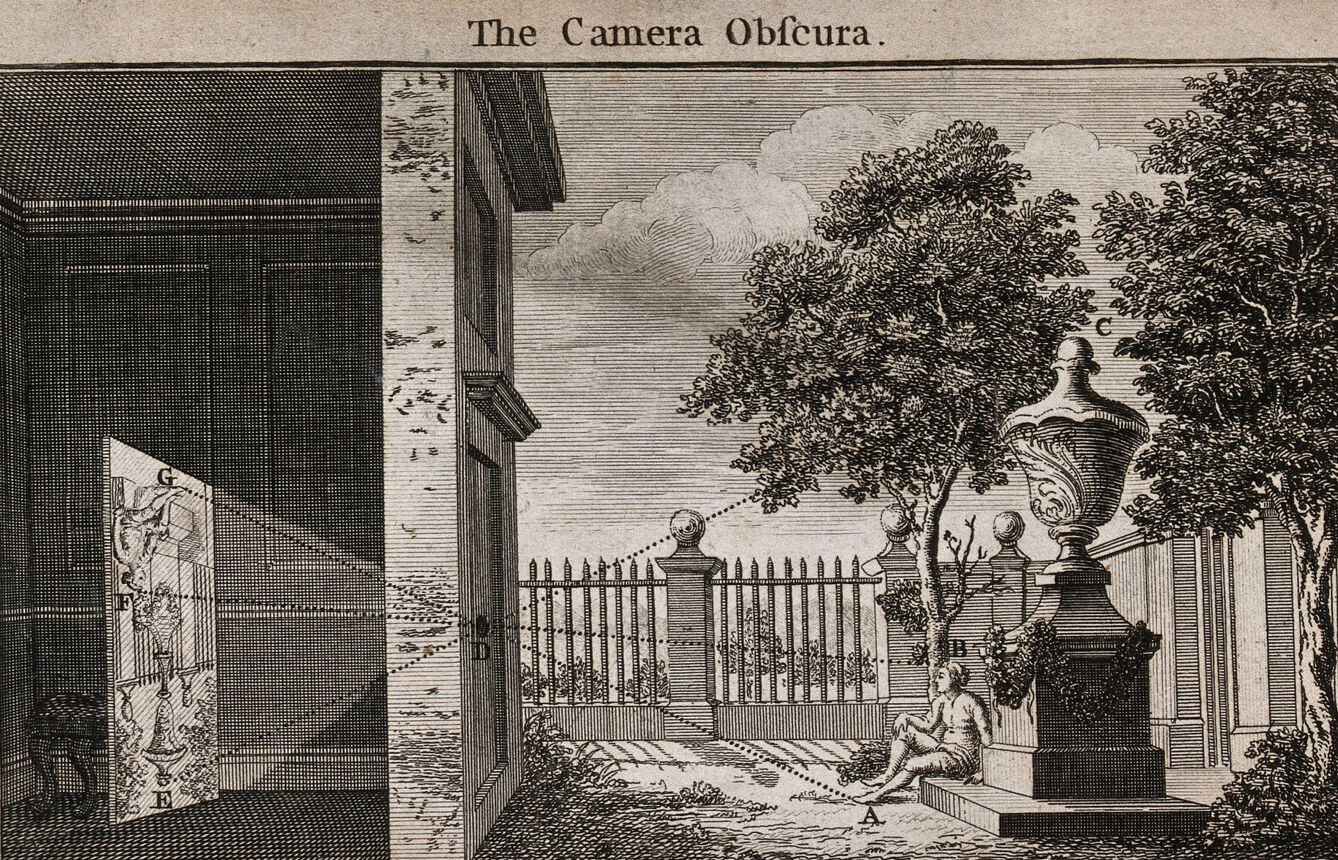 Source: Camera obscura, 1752. Source: Wellcome Collection The phenonemon has been known since antiquity, and there was a great deal of interest in it in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, when optics was becoming a modern science. Artists, for example, used them to achieve greater realism in when painting landscape scenes. The experiments with the camera obscura in this period ultimately led to the development of modern photography in the first decades of the nineteenth century. A modern photographic camera is in essence a small camera obscura with a means of making a permanent record, chemical or digital, of the image projected through a lens. Here you might discover the Waves and Fluctuations of the Water in strong and proper Colours, with the Picture of a Ship entering at one end, and sailing by Degrees through the whole Piece. On another there appeared the Green Shadows of Trees, waving to and fro with the Wind, and Herds of Deer among them in Miniature, leaping about upon the Wall. I must confess, the Novelty of such a Sight may be one occasion of its Pleasantness to the Imagination, but certainly the chief Reason is its near Resemblance to Nature, as it does not only, like other Pictures, give the Colour and Figure, but the Motion of the Things it represents.
Source: Camera obscura, 1752. Source: Wellcome Collection The phenonemon has been known since antiquity, and there was a great deal of interest in it in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, when optics was becoming a modern science. Artists, for example, used them to achieve greater realism in when painting landscape scenes. The experiments with the camera obscura in this period ultimately led to the development of modern photography in the first decades of the nineteenth century. A modern photographic camera is in essence a small camera obscura with a means of making a permanent record, chemical or digital, of the image projected through a lens. Here you might discover the Waves and Fluctuations of the Water in strong and proper Colours, with the Picture of a Ship entering at one end, and sailing by Degrees through the whole Piece. On another there appeared the Green Shadows of Trees, waving to and fro with the Wind, and Herds of Deer among them in Miniature, leaping about upon the Wall. I must confess, the Novelty of such a Sight may be one occasion of its Pleasantness to the Imagination, but certainly the chief Reason is its near Resemblance to Nature, as it does not only, like other Pictures, give the Colour and Figure, but the Motion of the Things it represents.
We have before observed, that there is generally in Nature something more Grand and August, than what we meet with in the Curiosities of Art. When therefore, we see this imitated in any measure, it gives us a nobler and more exalted kind of Pleasure than what we receive from the nicer and more accurate Productions of Art. On this Account our English Gardens are not so entertaining to the Fancy as those in France and Italy, where we see a large Extent of Ground covered over with an agreeable mixture of Garden and Forest, which represent every where an artificial Rudeness, much more charming than that Neatness and Elegancy Verso which we meet with in those of our own Country. It might, indeed, be of ill Consequence to the Publick, as well as unprofitable to private Persons, to alienate so much Ground from Pasturage, and the Plow, in many Parts of a Country that is so well peopled, and cultivated to a far greater Advantage. But why may not a whole Estate be thrown into a kind of Garden by frequent Plantations, that may turn as much to the Profit, as the Pleasure of the Owner? A Marsh overgrown with Willows, or a Mountain shaded with Oaks, are not only more beautiful, but more beneficial, than when they lie bare and unadorned. Fields of Corn make a pleasant Prospect, and if the Walks were a little taken care of that lie between them, if the natural Embroidery of the Meadows were helpt and improved by some small Additions of Art, and the several Rows of Hedges set off by Trees and Flowers, that the Soil was capable of receiving, a Man might make a pretty Landskip of his own Possessions.
Writers who have given us an Account of China, tell us the Inhabitants of that Country laugh at the Plantations of our Europeans, which are laid out by the Rule and Line; because, they say, any one may place Trees in equal Rows and uniform Figures. They chuse rather to shew a Genius in Works of this Nature, and therefore always conceal the Art by which they direct themselves. They have a Word, it seems, in their Language, by which they express the particular Beauty of a Plantation that thus strikes the Imagination at first Sight, without discovering what it is that has so agreeable an Effect. Our British Gardeners, on the contrary, instead of humouring Nature, love to deviate from it as much as possible. Our Trees rise in Cones, Globes, and Pyramids. We see the Marks of the Scissars upon every Plant and Bush. I do not know whether I am singular in my Opinion, but, for my own part, I would rather look upon a Tree in all its Luxuriancy and Diffusion of Boughs and Branches, than when it is thus cut and trimmed into a Mathematical Figure; and cannot but fancy that an Orchard in Flower looks infinitely more delightful, than all the little Labyrinths of the more finished Parterre. But as our great Modellers of Gardens have their Magazines of Plants to dispose of, it is very natural for them to tear up all the beautiful Plantations of Fruit Trees, and contrive a Plan that may most turn to their own Profit, in taking off their Evergreens, and the like Moveable Plants, with which their Shops are plentifully stocked.
O.

